In petrochemical, power plant, and large-scale facility industries, “vibration” and “thermal expansion and contraction” are two primary enemies of piping systems and ducts. Failure to properly manage these forces can lead to metal fatigue, weld fractures, and complete production line shutdowns. The engineering solution to this challenge is the use of a Vibration Absorber or expansion joint.
In this specialized article from Klevers Aryana, drawing on two decades of experience and current global standards (EJMA and FSA), we will conduct a detailed examination of the types of vibration absorbers, their technical differences, and how to select them correctly.
What Exactly Does a Vibration Absorber Do?
A vibration absorber, or in more technical terms, an Expansion Joint, is a component designed to absorb movements caused by temperature changes (Thermal Expansion), vibrations from pumps and compressors, and minor misalignments in the installation of pipelines.
The main functions of this equipment are:
- Absorbing Vibrations: Preventing the transmission of vibrations from motors to the pipe body.
- Compensating for Expansion and Contraction: Managing the change in length of pipes due to temperature fluctuations.
- Reducing Noise: Especially in rubber and fabric models.
- Compensating for Misalignment: Correcting minor installation errors.
For more reading on basic concepts, you can review the article Vibration Absorber: Types, Applications, Selection and Buying Guide – 2025.
Types of Vibration Absorbers by Material and Application
Choosing the correct material is the most critical part of the purchasing process. Vibration absorbers are generally divided into three main categories:
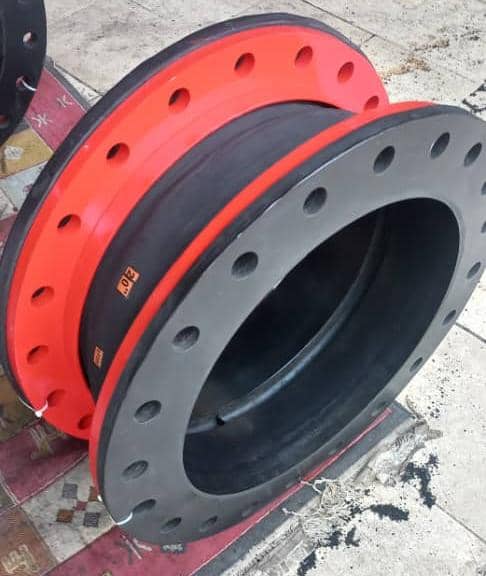
1. Rubber Expansion Joint
These models are used for low temperatures (typically up to 120°C) and medium working pressures. The main body is made of elastomers (EPDM, NBR, Viton) reinforced with fibers or steel wire.
- Advantages: Excellent vibration and sound absorption, resistance to chemical corrosion, ability to move in all directions.
- Application: HVAC systems, water pumps, and water treatment industries.
If you need more detailed information about this model, we suggest you read the Rubber Expansion Joint page.

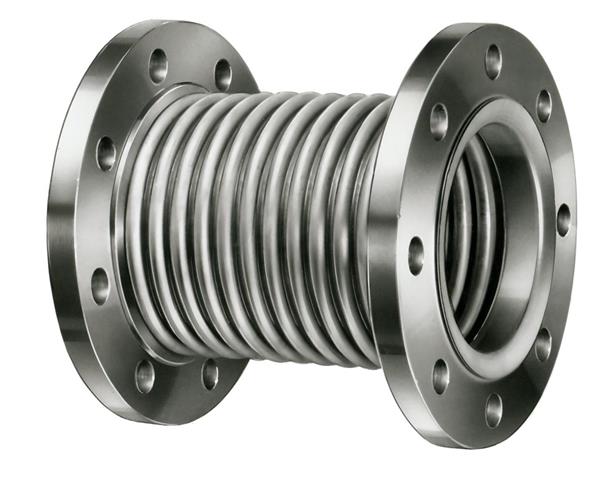
2. Metal or Accordion Expansion Joint (Metal Bellows)
When temperature and pressure exceed the tolerance of rubber, metal expansion joints come into play. These joints are typically made of stainless steel (SS304, SS316) or special alloys like Inconel.
- Advantages: Withstands very high temperatures (up to 1000°C+), resistance to heavy pressures.
- Disadvantages: Transmits high-frequency sound and vibration (unlike rubber models).
- Application: Turbine exhaust outlets, high-pressure steam lines.
For a specialized review of this category, the article Introduction to Metal Expansion Joints: Variety, Advantages, Application, and Buying Guide is a comprehensive reference for you.

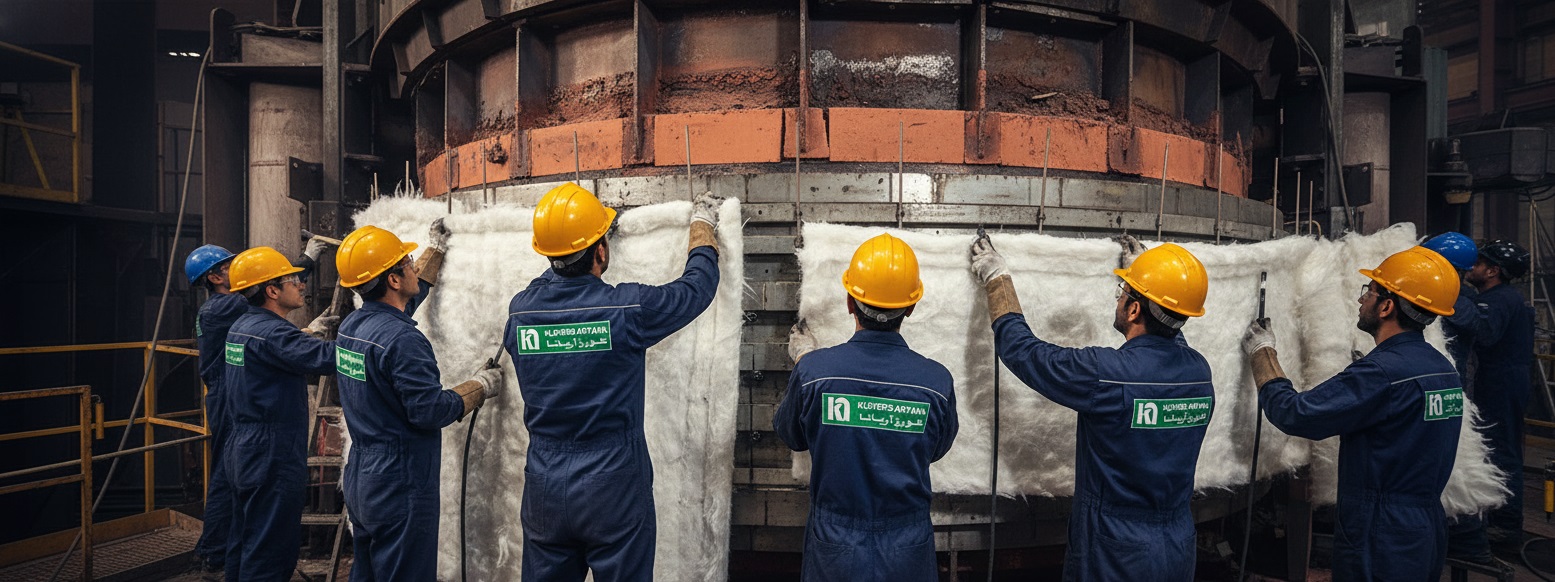
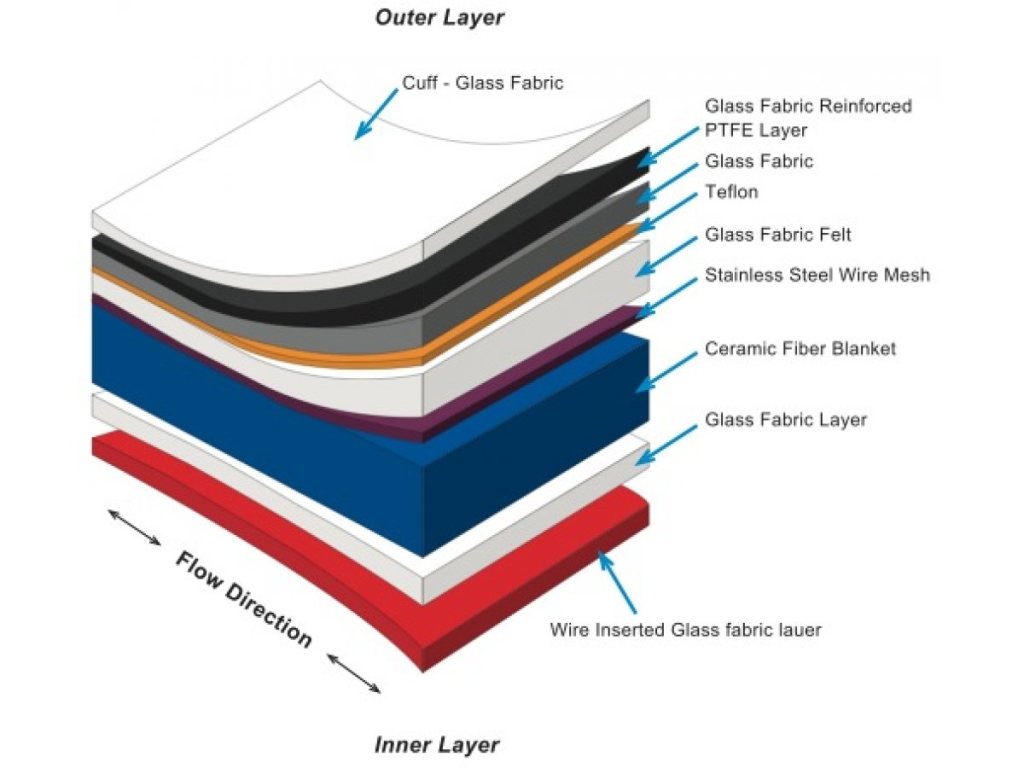
3. Fabric Expansion Joint
This category of expansion joints is designed for low-pressure hot gas ducts. These joints are composed of multiple layers of refractory fabric, fiberglass, and thermal insulation.
- Key Feature: Ability to withstand extremely high temperatures (up to 1200°C in multi-layer designs) and great flexibility in large dimensions.
- Application: Power plants, cement kilns, steel mills, and petrochemical industries.
See the technical details and layering of these products on the Fabric Expansion Joints: Introduction, Advantages, and Purchase Consultation page.

Technical Comparison Table of Vibration Absorber Types
| Feature | Rubber Expansion Joint | Metal Expansion Joint (Bellows) | Fabric Expansion Joint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 120°C | Up to 1000°C | Up to 1200°C |
| Pressure Tolerance | Medium/High | Very High | Low (Duct specific) |
| Vibration Absorption | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Depends on rubber type | Good (with alloy selection) | Excellent (with Teflon layer) |
| Repair Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
5 Critical Criteria in Selecting a Vibration Absorber (The STAMP Standard)
According to global standards like the FSA (Fluid Sealing Association), you must follow the STAMP rule for correct selection:
- S (Size): Pipe diameter and installation dimensions.
- T (Temperature): Fluid and ambient temperature. (Crucial for choosing between metal and fabric).
- A (Application): Type of connected equipment (pump, turbine, fan).
- M (Media): Type of fluid (water, steam, acidic gas, abrasive particles).
- P (Pressure): Maximum working pressure and system test pressure.
Expert Tip: In systems where the fluid contains abrasive solid particles (like in cement plants), the use of a Baffle or internal liner in metal and fabric expansion joints is mandatory to prevent direct abrasion of the bellows or fabric layers.
Installation and Maintenance: The Achilles’ Heel of Vibration Absorbers
Purchasing the best brand of vibration absorber without proper installation is a waste of capital. A common mistake is not using Control Rods in high-pressure rubber expansion joints, which leads to over-extension.
Also, in fabric models, the method of tightening clamps and the direction of layer overlap against the airflow are critical. To prevent premature failures, be sure to read the article Golden Tips for Installation and Maintenance of Expansion Joints. Preventive maintenance can increase the life of your equipment by up to 3 times.
Why Klevers Aryana’s Vibration Absorbers?
The refractory and insulation industry is one based on “trust” and “technical knowledge.” Klevers Aryana Company, with over 20 years of distinguished experience in supplying and manufacturing refractory materials and various Expansion Joints, has been a business partner to Iran’s core industries.
What sets us apart:
- Custom Design: We design and manufacture vibration absorbers precisely based on your site’s drawings and operating conditions (temperature, pressure, gas type).
- European Materials: Use of refractory fabrics and ceramic fibers with globally standard grades.
- Engineering Team: Free product selection consultation and installation supervision.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a vibration absorber and a shock absorber?
An Expansion Joint (vibration absorber) is designed to absorb thermal movements and continuous vibration, while a Shock Absorber is used to dampen sudden impacts (like water hammer).
2. What is the service life of a fabric expansion joint?
With correct layer selection and proper installation, they can last between 5 to 10 years under the toughest working conditions.
Need technical advice?
To select the most accurate type of vibration absorber for your project and receive an updated price list, contact Klevers Aryana’s technical experts now. We offer solutions that will minimize your repair and maintenance costs.
1 Contact Information: Contact Us Page
References:
- Fluid Sealing Association (FSA) – “Expansion Joints – Piping Technical Handbook”. Available at: fluidsealing.com
- Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association (EJMA) – “Standards of the Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association, 10th Edition”. Available at: ejma.org
- EagleBurgmann – “Fabric Expansion Joints Design Manual”.
- Garlock Sealing Technologies – “Rubber Expansion Joint Selection Guide”.
- ISO 15348:2002 – Pipework — Metal bellows expansion joints — General.





